Object: Block1
Block1 inherits all methods of Grid while it mainly focuses on generating/manipulating 1D grids formed by Line cells.
Constructor
-
Block1(): generates Grid of Block1 type -
Block1({ coord1 }, { coord2 }, N)generates a line between and which is made up of cells; all at a level marked as 0. By default, the cell-levels cannot go below 0. However, one can change that if masters in each direction are defined (-not defined).Code Block1 lin({0.2, 0.3, 0}, {0.8, 0.6, 0}, 20)Line 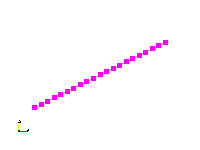
-
Block1(geo, N, <d0>, <d1>)generates a 1D array in the shape discribed by the geometry (see Geo1 using cells. Optional parameters and provide a new definition for start and end points for the arc in degrees. Note that . Following are some examples on the usage:Code Block1 circ(new Geo1Circle(Vec3(0.5, 0.75), 0.15), 40);Full circle (in CCW) 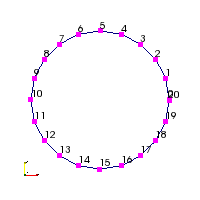
Code Block1 arc(new Geo1Circle(Vec3(0.5, 0.75), 0.15, 30, 120), 40);Arc () 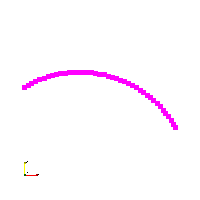
Code Block1 rotpenta(new Geo1Circle(Vec3(0.5,0.75), 0.15, 30, 400), 5);Pentagon (in CCW and rotated by ) 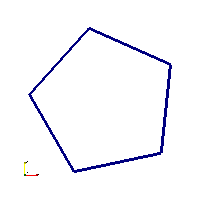
Code Block1 line2(new Geo1Sine(Vec3(0.2, 0.4), Vec3(0.5, 0.5), 0.1, 5), 50);Sinusodial 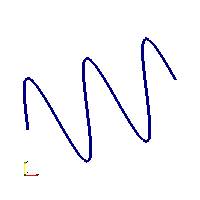
Note that one needs to make sure that the geometry created by
newcommand needs to be properly destroyed. Even though above examples provide one line statements; it is better to follow a proper decleration of a geometry which deleted from the memory by a properdeletecommand as follows:
1
2
3
4
auto tmp_geo = new Geo1Sine(Vec3(0.2, 0.4), Vec3(0.5, 0.5), 0.1, 5);
Block1 line2(tmp_geo, 50);
delete(tmp_geo);
Block1(, delta)produces connected lines between all supplied coordinates . If the first and the last coordinates are the same, it closes the loop properly. If is provided (non-zero) then cells are refined until all have a length smaller than . This is especially useful if a geometry needs to be defined purely based on coordinates; i.e. NACA airfoils.
Specific methods
resolve(delta)brings all cell lengths to a level closer to (a double).add(Geo, N)adds a new geometry which is made up of cells to an existing geometry. If first vertex point of the added geometry is the same as the last vertex of the existing geometry, new geometries become linked through those vertices. Otherwise, a separate geometry is combined into the existing one.add(Block1)adds vertices and cells into the one this method is called from.add(s0, s1, N, f)adds a new geometry defined by the parametric function f (similar to Geo) to the current geometry
Following methods are yet to be defined:
addVol(Block1)will involve merging areas enclosed by two grid (Block1 and current grid). Requires changing topologies.subVol(Block1)will involve removing areas enclosed by two grids; i.e. removing a triangular pie from a circle.trans(dir, distance)will involve translating vertex points in a particular direction () by given distance ().rot(x0, norm, theta)will involve rotating vertex point locations along an axis passing through in the direction of () by an angle prescribed by .rotate(x0, norm, theta, N)will create a 3D surface by rotating cells around a axis passing through in the direction of () by an angle prescribed by . The rotation angle will be discretized by cells.extrude(norm, double dist, N)will create a 3D surface by extruding cells in the direction defined by by a length defined by . There will cells in the direction of extrusion.