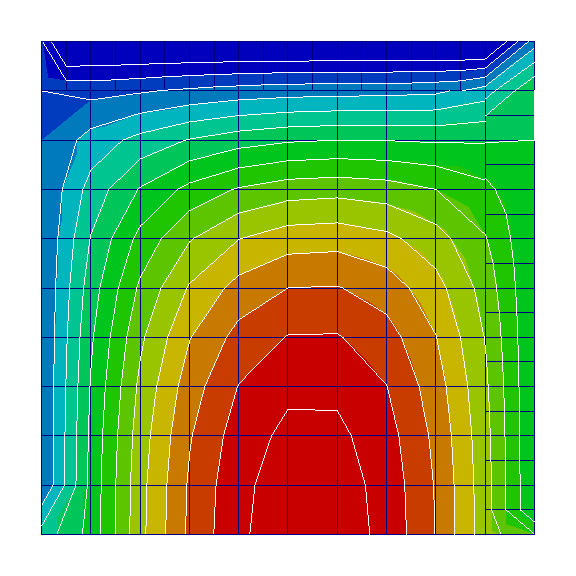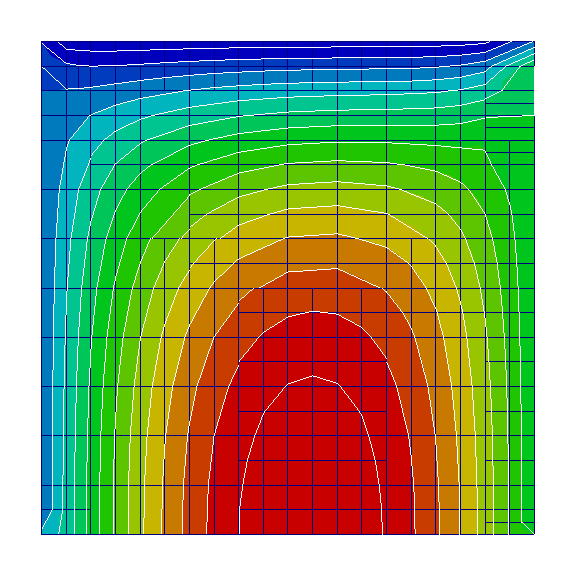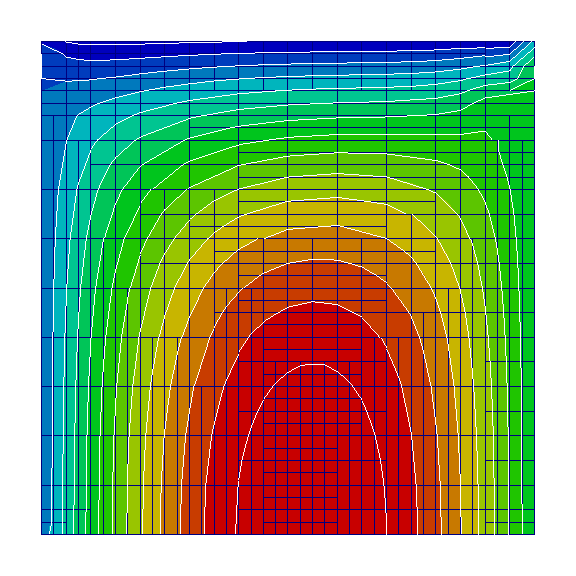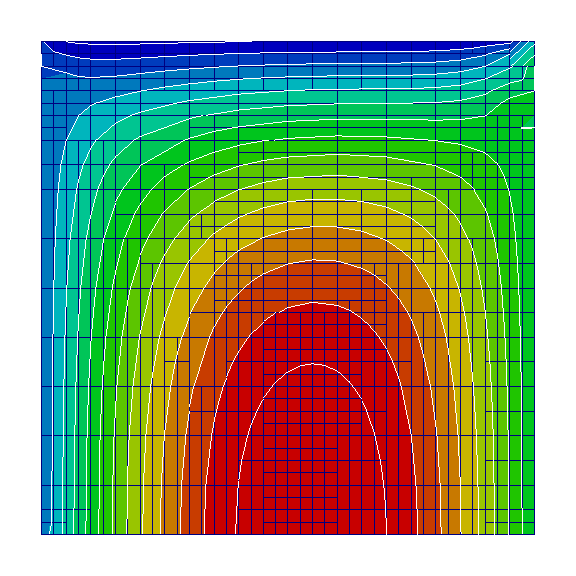
Heat equation in the following form is to be solved on a unit domain:
$$\vec{\nabla} \cdot (k \vec{\nabla} T) + \dot q_{o} = 0$$
exposed to following boundary conditions:
- Top wall:
- Bottom wall:
- Right wall:
- Left wall:
with the following set of parameters:
, , ,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
// Problem parameters
auto k = 2.0; auto qdot = 5e3; auto h = 50; auto Tinf = 20;
// Grid
Block2* grid = new Block2({0, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 0}, 10, 10);
grid->levelHighBound[0] = 2;
grid->levelHighBound[1] = 2;
grid->addVar("T");
// Variables
auto T = grid->getVar("T");
// Linear solver
T->solver = "BiCGSTAB";
T->itmax = 1000;
T->set(100);
// Boundary conditions
T->setBC("south", "grad", 0);
T->setBC("north", "grad", -h/k*Tinf, h/k);
T->setBC("east", "val", 200);
T->setBC("west", "val", 100);
for (auto i = 0; i< 4; ++i) {
grid->solBasedAdapt2(grid->getError2(T), 2e-3, 2e-1);
grid->adapt();
// Equation
grid->lockBC(T);
T->solve( grid->laplace(k)
+ grid->source(0, qdot) );
grid->unlockBC();
grid->writeVTK("heat");
}
delete(grid);
Above code produces the following result: